Module 6: Selecting and evaluating digital resources and tools
The aim of this module is to equip learners with the knowledge and skills necessary to effectively identify, assess, and utilize digital resources and tools in educational settings. This module aims to provide learners with the ability to critically evaluate the suitability, relevance, and quality of digital resources, ensuring that they can make informed decisions to enhance teaching and learning experiences.
Additionally, the module aims to foster an understanding of the importance of selecting and evaluating digital resources in meeting the diverse needs of learners.
Learning Outcomes
- You will understand key criteria such as relevance, accuracy, credibility, accessibility, and usability. This will enable you to make informed decisions when selecting resources and tools for your teaching or learning needs.
- You will evaluate a digital resource based on the identified criteria, considering their alignment with specific learning objectives and catering to diverse learner needs.
- You will cultivate a proactive approach towards digital resources and tools evaluation and selection, emphasizing continuous improvement and adaptability in response to evolving advancements.
Understanding the role of digital resources and tools is key for maximizing their impact in education. It involves leveraging technology to personalize learning, foster collaboration, and improve educational outcomes.
When evaluating digital resources, key criteria include relevance to learning objectives, accuracy of information, credibility of the content source, accessibility for diverse learners, and usability for enhanced learning experiences. These criteria ensure the quality and suitability of resources for effective teaching and learning outcomes.
You will have the opportunity to apply the concepts of relevance, accuracy, credibility, accessibility, and usability to evaluate a digital resource of your choice.
In a short case study, we’ll explore how a VET educator Maria utilized key criteria for evaluating digital resources to enhance learning experiences for diverse learners in a vocational education setting.
The role of digital resources and tools
- Digital resources and tools allow educators to create customized learning paths based on individual student needs, preferences, and learning styles. Through adaptive learning platforms and personalized feedback mechanisms, students can progress at their own pace, receive targeted interventions, and access resources that cater to their specific learning requirements.
- The integration of interactive multimedia content into teaching practices can significantly enhance student engagement and motivation. These tools provide immersive and hands-on learning experiences, making learning more enjoyable, relevant, and impactful for students of all ages.
Digital tools enable fast collaboration and communication among students, educators, and experts across the globe. Online platforms break down geographical barriers, allowing for real-time interactions, knowledge sharing, peer learning, and the development of global learning communities.
Key Criteria for evaluation
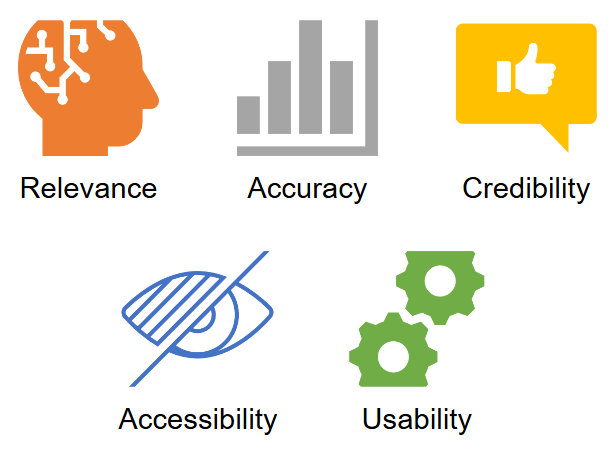
Relevance
Definition
Relevance in digital resource selection refers to the degree to which a resource aligns with the specific learning goals, objectives, and needs of a given educational context.
Why is it important?
- Alignment with learning goals: Relevant resources directly contribute to achieving the desired learning outcomes and goals set for a particular course or educational activity.
- Engagement and motivation: When resources are relevant to learners’ interests, backgrounds, and objectives, they are more likely to be engaged and motivated to learn.
- Efficient use of resources: Relevant resources optimize the use of time, effort, and resources by focusing on content that directly supports the educational objectives.
- Personalized learning experience: Tailoring resources to the specific needs and preferences of learners enhances the effectiveness of instruction and promotes personalized learning experiences.
- Real-world application: Relevant resources often bridge theory with real-world applications, enabling learners to apply their knowledge and skills in practical contexts.
Accuracy
Background
Definition
Accuracy in digital resources refers to the degree of correctness, truthfulness, and reliability of information presented within the resource.
How to verify accuracy?
- Fact-checking: Verify information by cross-referencing with reputable sources, checking for supporting evidence, and examining the credibility of the information provider.
- Cross-referencing sources: Compare information across multiple reliable sources to confirm consistency and accuracy.
- Evaluating data quality: Assess the reliability of data sources, validity of research methods, and relevance of data to the topic or subject matter.
Credibility
Definition
Credibility in digital resources refers to the trustworthiness, authority, and reliability of the information presented.
How to verify accuracy?
Factors that influence credibility
- Author credentials: Assess the expertise, qualifications, and reputation.
- Publication source: Evaluate the credibility and trustworthiness of the source.
- Peer review: Consider whether the content has undergone peer review .
How to achieve credibility
- Prefer information from reputable sources known for accurate and unbiased content.
- Be aware of potential biases in the content.
- Examine the author’s expertise, citations, and references.
Why is it important?
- Inclusivity: Ensures that all learners, regardless of their abilities, can access and engage with learning materials.
- Equal opportunity: Provides equal access to education and learning opportunities for everyone.
- Compliance: Meets legal requirements and standards such as WCAG (Web Content Accessibility Guidelines).
How to ensure accessibility?
- Ensure that digital resources are compatible with screen reading software.
- Provide alternative formats such as text transcripts for videos, accessible PDFs, and tactile graphics.
- Implement clear navigation structures, headings, and labels to help users navigate content easily.
Accessibility
Definition
Accessibility in digital resources refers to ensuring that content and tools are usable by individuals with diverse abilities and needs.
Usability
Definition
Usability refers to the ease of use and user-friendliness of digital tools, platforms, and resources.
Factors that influence usability
- User interface design: Designing intuitive interfaces with clear layouts and organized content.
- Navigation structure: Creating logical paths within digital resources.
- User feedback: Incorporating feedback mechanisms to understand user preferences.
User-friendly resources examples
- Interactive learning modules: Engaging modules with clear instructions and interactive elements.
- Mobile-friendly platforms: Platforms optimized for mobile devices with responsive design.
- Collaborative tools: Tools that facilitate collaboration among learners.
Answer the following questions based on what you learned in the previous slides:
- What is the difference between accuracy and credibility?
- How does relevance contribute to the evaluation of digital resources, and can you provide an example of a relevant resource that enhances learning outcomes?
- In what ways does accessibility impact the usability of digital resources, and what are two accessibility considerations educators should prioritize when selecting resources?
- Can you assess the credibility of a hypothetical digital resource based on the author’s credentials, publication source, and peer review status? Please explain your rationale for determining its credibility or lack thereof.
How does usability influence the effectiveness of digital tools and resources in supporting learning experiences, and can you identify user-friendly features that enhance usability and learner engagement?
Activity 2: Digital resource evaluation
Objective: Apply the concepts of relevance, accuracy, credibility, accessibility, and usability learned in the presentation to evaluate a digital resource or tool of your choice.
Follow the steps described on the upcoming slides!
Activity 2: Steps to follow
Step 1: Choose a digital resource (or tool): Select a website, online article, video, or any digital resource relevant to your field of study or interest.
Step 2: Go through the evaluation criteria:
- Relevance: Assess how well the resource aligns with your learning objectives or information needs.
- Accuracy: Verify the correctness of facts, data, and information presented in the resource.
- Credibility: Investigate the author’s credentials, publication source, and any indications of bias or reliability.
- Accessibility: Consider how accessible the resource is for users with disabilities, such as screen reader compatibility or alternative text for images.
- Usability: Evaluate the user-friendliness of the resource in terms of navigation, layout, and interactive features.
Step 3: Analysis and documentation:
- Create a document or worksheet to record your evaluation findings for each criterion.
- Write a brief analysis discussing how each criterion influenced your overall assessment of the resource.
- Include specific examples or screenshots from the resource to support your evaluation points.
Step 4: Reflection:
- Reflect on the challenges encountered during the evaluation process and how you addressed them.
- Consider how the concepts of relevance, accuracy, credibility, accessibility, and usability interplay in determining the quality of digital resources.
Tips for VET Educators

Prioritize digital resources and tools that are user-friendly and intuitive for both educators and learners. Look for platforms with clear navigation, organized content, and user-friendly interfaces to enhance usability.
Ensure that the digital resources selected align closely with the learning objectives, curriculum standards, and specific needs of your learners. Verify relevance by checking how well the content addresses the intended learning outcomes and engages students effectively.
Thoroughly assess the credibility and accuracy of digital resources before incorporating them into teaching materials. Verify the author’s credentials, check the publication source, and review the accuracy of information presented to maintain academic integrity and reliability.
Choose digital resources and tools that prioritize accessibility features such as screen reader compatibility, alternative formats for content (e.g., captions for videos, transcripts), and usability for learners with diverse needs. Ensure that all students can access and engage with the materials effectively.
Tips for VET Educators
Scenario
Maria is a vocational education professional who is responsible for teaching a course on digital literacy and employability skills to a group of adult learners seeking to improve their job prospects.
Maria wants to select and evaluate digital resources and tools that align with the project’s goals and meet the diverse needs of her learners.
Challenges
Maria’s main challenges stem from the diverse backgrounds and skill levels of her adult learners. She must select digital resources and tools that accommodate varying levels of digital literacy and employability skills.
Furthermore, amidst the abundance of available resources, Maria must discern those that are not only relevant to the course curriculum but also uphold standards of quality and credibility.
She also has to ensure the accessibility and user-friendliness of the chosen resources, catering to learners with disabilities and facilitating integration into the learning environment.
Case Study
Actions
To address the challenges posed by the diverse learner needs, Maria conducted a needs assessment. This involved assessing her students’ digital literacy levels, career aspirations, and preferred learning styles.
Afterwards, Maria curated a selection of resources and tools tailored to her learners’ specific requirements. Subsequently, Maria engaged in research and evaluation, exploring various online platforms, repositories, and educational websites. She carefully assessed each digital resource based on criteria such as relevance to the course content, credibility, ease of use, and accessibility. Additionally, Maria actively collaborated with her colleagues.

Outcomes
Maria’s efforts resulted in significant outcomes, impacting both the learning experience and the acquisition of employability skills among her students. By carefully selecting resources and tools tailored to her learners’ needs, Maria created a highly personalized and engaging learning environment.
This tailored approach fostered engagement and participation, as students interacted with course materials and applied newfound skills in real-world scenarios.
After that, learners experienced improvements in their employability skills. Maria’s dedication and strategic approach also received positive feedback.

- How did Maria address the challenge of catering to diverse learner needs when selecting digital resources and tools for her vocational education course?
- What steps did Maria take to ensure the relevance, quality, accessibility, and usability of the digital resources and tools she integrated into her teaching practice?
- Reflecting on Maria’s approach and outcomes, how might you apply similar strategies to enhance digital resource selection and evaluation in your own educational context?
Assessment
Conclusion
In this module, we covered key considerations regarding the selection and evaluation of digital resources including relevance, accuracy, credibility, accessibility, and usability.
We discussed strategies for assessing relevance based on learning goals and specificity, methods for verifying accuracy such as fact-checking and cross-referencing, factors influencing credibility like author credentials and peer review, considerations for ensuring accessibility such as screen reader compatibility and alternative formats, and factors impacting usability including user interface design and navigation structure.
By integrating these insights into teaching practices, educators can create a more engaging, inclusive, and effective digital learning environment for all learners, promoting enhanced learning outcomes and student engagement. Thank you for participating in this module!

References
- Kalaš, I. (2013). Premeny školy v digitálnom veku [Transformations of school in the digital age]. Slovenské pedagogické nakladateľstvo.
- Folwarczná, I. (2010). Rozvoj a vzdělávání manažerů [Development and education of managers]. Grada.
- Pokorný, M. (2009). Digitální technologie ve výuce 2 [Digital technologies in teaching 2]. Computer Media.
- Černý, M. (2019). Digitální kompetence v transdisciplinárním nahlédnutí [Digital competence in a transdisciplinary perspective]. Munipress.
- Zounek, J., & Juhaňák, L. (2016). E-learning – Učení (se) s digitálními technologiemi [E-learning – Learning with digital technologies]. Wolters Kluwer.
- Barešová, A. (2012). E-learning ve vzdělávání dospělých [E-learning in adult education]. VOX.
- Černý, M. (2018). Pedagogicko-psychologické otázky online vzdělávání [Pedagogical-psychological issues of online education]. Munipress.

Funded by the European Union. Views and opinions expressed are however those of the author(s) only and do not necessarily reflect those of the European Union or the European Education and Culture Executive Agency (EACEA). Neither the European Union nor EACEA can be held responsible for them. Project Number:2022-2-IE01-KA220-VET-